Phonetics, a fascinating field within linguistics, delves into the study of the physical attributes of speech sounds, encompassing their production and the way they are perceived by our auditory system. Its primary focus lies in unravelling the intricate processes through which humans generate and comprehend speech sounds across different languages.
Now, let’s explore some key facets of phonetics:
Articulatory Phonetics: This captivating branch of phonetics places its emphasis on the physical production of speech sounds by our remarkable vocal apparatus. It meticulously examines the intricate movements and positions of our speech organs, such as the tongue, lips, and vocal cords, during the act of speaking. By dissecting these articulatory mechanisms, articulatory phonetics unveils the secrets behind the creation of various sounds through the manipulation of these remarkable articulators.
Acoustic Phonetics: Enter the enchanting realm of acoustic phonetics, where the physical properties of sound waves produced during speech take centre stage. This branch meticulously scrutinises the frequency, intensity, and duration of these sound waves, unravelling their unique characteristics. Through acoustic analysis, we gain a deeper understanding of speech sounds, allowing us to describe and categorise them based on their distinct acoustic properties.
Auditory Phonetics: Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the realm of auditory phonetics, where we explore the intricate ways in which humans perceive and interpret speech sounds. This branch delves into the marvelous processes through which our ears and brains process incoming auditory information, enabling us to recognize and comprehend speech. Auditory phonetics plays a pivotal role in unravelling the perceptual aspects of speech, shedding light on the remarkable ways in which our minds decode the rich tapestry of sounds that surround us.
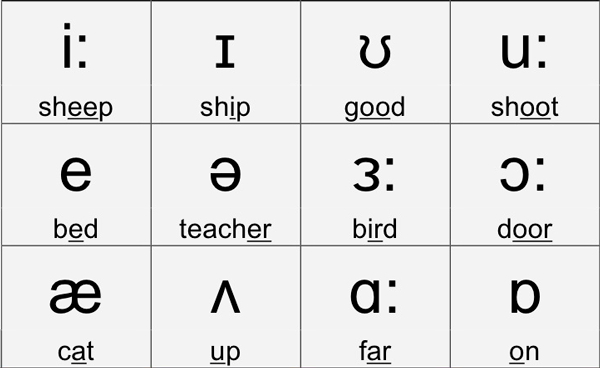
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) serves as a standardised system of symbols utilised to represent the various sounds found in spoken language. By transcribing spoken language into a written form, the IPA accurately captures the sounds produced. Linguists and language learners frequently rely on the IPA to describe and compare word pronunciation across different languages.
Phonetic transcription involves the representation of spoken language using symbols from the IPA. This transcription aids linguists and language professionals in precisely capturing word pronunciation and speech sounds.
Phonetics further distinguishes between segmental features, which encompass individual speech sounds or segments, and suprasegmental features, which encompass intonation, stress, and rhythm. These suprasegmental features contribute to the overall prosody of speech.
In essence, phonetics is a multidisciplinary field that combines elements of physics, anatomy, psychology, and linguistics to study the production, transmission, and perception of speech sounds. It plays a pivotal role in comprehending the fundamental components of spoken language across diverse cultures and languages.